
The online market is becoming more competitive every day. An increasing number of online businesses are competing for the same customers.
Therefore, online business owners don't have the luxury of tolerating website issues like crashes. The more your website crashes, the more customers you lose. Even poor page load times increase bounce rates by up to 53%.
Essentially, you have no option but to optimize your website and prevent crashes or resolve them as quickly as possible. This article will discuss five common issues responsible for website crashes and how they can be resolved.
So, if you're wondering why websites crash, here are the answers:
1. Web Code Errors
Web code errors are usually caused by an issue with site development, such as coding on a page. They may occur during a website's development, design, or maintenance.
The image below shows that even minor punctuation like angle brackets (<>) can generate an error message, resulting in a website crash.

For a website that has been live for quite some time, maintenance or a plugin update can cause the website to crash. In such a case, the quality assurance team must carefully examine and approve all the static or dynamic content.
If your website is in its initial phase, the staging environment is the best place and time to review and revise the changes before the website goes live.
Essentially, for revenue-generating websites, site owners should leave the technical aspect to the professionals. They are familiar with the code and can help prevent any major or common issues related to web code, significantly improving the website or app performance.
2. Malicious Attacks
A website is only as strong as its weakest security link. Unfortunately, websites can be easy targets for cybercriminals looking to steal data and passwords or even shut down a business.
This security breach is caused by malicious attacks, such as distributed denial of service (DDoS), SQL injection, and cross-site scripting.
Hackers with malicious intent break into a site through weak links, often resulting in a website crash. They use automated bots to bombard website servers with requests from unknown traffic sources until they can no longer handle the load and fail to perform properly.
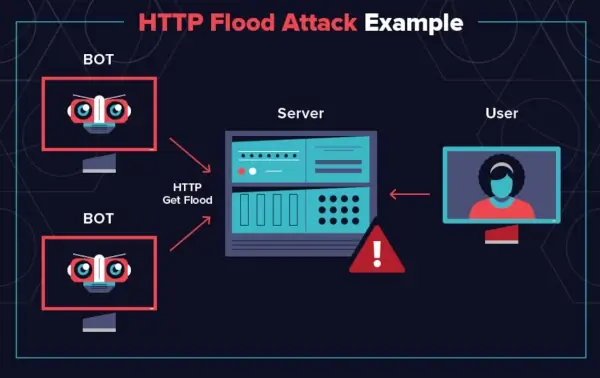
Using a reliable hosting plan with secure servers is the best way to avoid infecting your website with malicious attacks. Website owners can also utilize web application firewalls (WAFs), such as Azure WAF, Cloudflare WAF, etc. These WAFs scan all traffic sources going to and from their website for malicious activity and can block attacks in real time.
Furthermore, data or security breaches are not unusual for online users. Even surfing cautiously leaves some tracks for data brokers. They gather information from different sources, create your profile, and use it to sell or abuse. In such circumstances, online users can utilize privacy apps like Optery or Privacybee.
These apps search for the user's data online and manage to delete it or give them the tools for removal. These apps can help protect and save their personal information from identity theft.
Businesses can create these privacy apps and generate a QR code for app download so more people can take advantage of the opportunity to save their online profiles from data brokers. Additionally, learn how to edit a QR code to customize it for your audience's needs.
3. Server Errors
Server errors are caused by an overwhelming traffic load on the server. This usually happens when too many users try to connect to the site simultaneously, filling up the server's memory and causing the website to crash.
Why do websites crash due to server errors? Here are the common 5xx HTTP status code errors and what they mean:
- 500 Internal Server Error: The server cannot process the heavy database requests. A common cause could be a misconfiguration of the server, e.g., a malformed .htaccess file.
- 502 Bad Gateway: The 502 status code, also known as the Bad Gateway error, means that the server is a gateway or proxy server, and it is not receiving a valid response from the backend servers that should fulfill the request.
- 503 Service Unavailable: This can be caused by the temporary overload of the server or a firewall issue.
- 504 Gateway Timeout: This error occurs when the server acts as a gateway and does not receive a timely response.
These errors can be frustrating for website owners and visitors, as it can often be unclear what is causing the error. However, some steps can be taken to mitigate server errors.
- Leverage a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute content across multiple servers.
- Use caching to reduce the load on the server
- Optimize code and database queries
It is essential to have a reliable hosting plan to prevent server crashes. The more reliable the domain hosting is, the less likely a website will crash due to too many users accessing it simultaneously.
Additionally, caching services like Cloudflare can help reduce your server's load and optimize website performance for real visitors.
It is essential to monitor server capacity and its performance and continually monitor your servers for any key bottlenecks that might cause the website to increase the actual load time.
If a website is experiencing intense spikes in traffic, the best practice is to increase server resources, such as server capacity, to accommodate the load better. Additionally, regularly updating software and plugins can help keep everything running smoothly.
By taking these precautions, website owners can reduce the chances of their site crashing due to a server error. Most importantly, even if errors do occur, they can be quickly identified and rectified.
Finally, always contact your service provider in case of an emergency. They may already have a crash prevention strategy, and reaching out to them will be the quickest solution to any server-related problem.
4. Unforeseen Traffic Spike
Genuine spikes in traffic are generally considered a good thing. Most businesses will do everything they can to raise their traffic, whether it's expanding their SEO budget, increasing paid ads, or even buying Instagram followers to amplify their social campaigns.
However, a sudden spike in traffic that your website was unprepared to handle can lead to severe problems. A website crash is one of the most common issues associated with an unforeseen online traffic spike.
This occurs when the server that hosts the website is overwhelmed by the number of requests and cannot process them all promptly. As a result, the site becomes unavailable to users.
The owner needs to perform load tests to determine whether the surge of traffic causes the issue. Load testing simulates a high traffic volume on a website to identify potential problems and common bottlenecks.
Website owners can run load tests to determine how well their site will perform under high-traffic loads. Additionally, users can perform performance testing to help identify potential issues that need addressing before large amounts of traffic occur.
There are several ways to mitigate the problem of an unforeseen traffic surge, including load balancing and caching. Load balancing ensures that traffic flow is evenly distributed across multiple servers. Caching stores frequently requested data to be quickly retrieved when needed.
Implementing these measures can prevent website crashes and keep them up and running even during periods of massive traffic.
5. Expired Domain
Domain names are registered through a registrar for a specific period of time, typically 1-3 years. After the expiration date, the domain name is placed back into the available pool of domains and can be registered again by any party.

If a website uses an expired domain for its main website or subdomain, it could crash the website. This is because search engines such as Google will often remove all results from a website if the domain name has expired and has been re-registered by someone else.
Website owners with a revenue-generating site should turn on the auto-renewal option to prevent such domain issues. Otherwise, check the domain's expiration date to ensure it remains active.
In Conclusion
Those mentioned above are the answers to why websites crash and how to avoid the commonly associated issues. Overall, the most significant way to prevent a website from crashing is to plan to deal with any web code errors, malicious attacks, server errors, unexpected sudden traffic spikes, and domain issues.
A content delivery network (CDN) can help distribute content across multiple servers and reduce the load on the main server. Caching can store frequently requested data and retrieve it quickly when needed. Ensure that the professionals managing your website's backend know about common hacker attacks, such as unwanted DDoS attacks.
By taking these precautions, website owners can create an environment conducive to ensuring their websites are secure and functioning optimally. These guidelines will facilitate website owners' providing a reliable user experience for new visitors and frequent customers, improving their customer journey.


 Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.