
Did you know that 88% of online consumers are less likely to return to a website after a bad user experience? This means that no matter how small, website errors can significantly impact your website's traffic and revenue. As a website owner or manager, it's crucial to identify and fix common errors to ensure your website runs smoothly and provides an exceptional user experience. But where do you start? With so many potential issues that can arise, it can be overwhelming to know what to prioritize.
So, if you're ready to take your website's performance to the next level and impress your users, keep reading. We'll provide you with the tools and knowledge you need to identify and fix common website errors and ensure your website provides the best possible user experience.
What Are The Common Website Errors And How To Fix Them?
1. Broken Links
Suppose, as a part of your marketing strategy, you get Instagram followers and share the landing page link with them to improve reach, but it takes you nowhere as the link is broken. Broken links can be a frustrating experience for users and can cause them to lose trust in your website. They can also negatively impact your search engine rankings, as search engines don't like indexing pages with broken links.
So, what causes broken links? Some common causes include:
- Updating or redesigning a website without updating internal links
- Deleting or moving a page without redirecting the URL
- External links that are no longer active
How to fix broken links?
To fix broken links, you can use a broken link checker tool to identify any links that are no longer working. Once you've identified these links, you can either remove them or redirect them to a new page.
If you use a content management system like WordPress, plugins can help you automatically find and fix broken links.
2. Slow Page Speed
Slow page speed can be a major issue for user experience and can cause visitors to leave your website before even seeing your content. In fact, a survey by Akamai found that 53% of website visitors will abandon a site if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
What can cause slow page speed? Some common causes include:
- Large image or video files that take a long time to load
- Poor website hosting
- Too many plugins or scripts running on a page
- Large amounts of unoptimized code
How to fix Slow page speed?
Slow page speeds can be a major problem for website owners, but there are several ways to improve your site's performance. One of the most effective methods is to compress and optimize any large image or video files on your site. Crop video tools can greatly help in this regard, as they allow you to quickly and easily edit your videos and reduce their file size without compromising quality.
Additionally, it's a good idea to optimize your website's code by minifying any unnecessary white space or code comments. This can help reduce the size of your website files and improve page speed.
Pro Tip: Sign up for a website monitoring service to get alerted as soon as your website gets connectivity or speed issues.
3. HTTP Errors
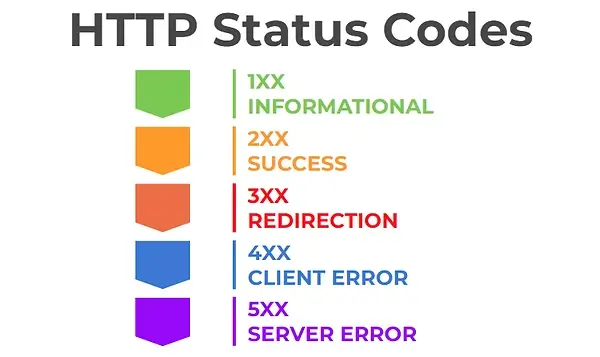
HTTP errors are also common website errors that can negatively impact user experience. HTTP errors occur when a user tries to access a web page that can't be found or accessed, displaying an error message. The most common HTTP errors are:
1. 404 Not Found Error - The 404 Not Found Error occurs when the web server cannot find the requested resource. This can happen if a page has been deleted or moved to a new URL.
Solution: Create a custom 404 error page that provides a user-friendly message to visitors and suggests other pages they might be interested in. Ensure that all links on your website are up-to-date and that any pages that have been moved are redirected to the new URL using a 301 redirect.
2. 500 Internal Server Error - The 500 Internal Server Error occurs when the server encounters an unexpected condition that prevents it from fulfilling the request made by the user.
Solution: This error can be caused by various issues, such as coding errors, server overload, or insufficient server resources. Check your server logs for error messages and fix any coding issues. If the problem is related to server resources, consider upgrading your hosting plan.
3. 403 Forbidden Error - The 403 Forbidden Error occurs when the user does not have permission to access the requested resource. This error is typically returned when the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it, leading to the 403 status code.
Solution: Check your file and directory permissions to ensure they are set correctly. Ensure there are no typos in the URL and the user is logged in with the appropriate permissions.
4. 401 Unauthorized Error - The 401 Unauthorized Error occurs when the user does not have the necessary authorization to access the requested resource.
Solution: Check your authentication settings to ensure they are set up correctly. Ensure that the user is logged in with the appropriate credentials and that any required permissions are granted.
5. 504 Gateway Timeout Error - The 504 Gateway Timeout Error occurs when the server acting as a gateway does not receive a response from the upstream server within a specified time frame.
Solution: This error can be caused by various issues, such as server overload or network connectivity problems. Check your server logs for error messages and ensure your server is configured to handle the expected traffic. If the issue concerns network connectivity, contact your hosting provider for assistance.
4. Mobile Responsiveness Issues
With over half of all internet traffic coming from mobile devices, your website must be optimized for mobile use. Mobile responsiveness issues, such as pages that don't fit on a mobile screen or buttons too small to click, can negatively impact user experience and harm your search engine rankings.
How to fix mobile responsiveness issues?
To fix mobile responsiveness issues, you can use a mobile responsiveness tool to identify any issues on your website. You can also try using responsive design techniques, such as using mobile-friendly font size and ensuring all buttons are large enough to be easily clicked on a mobile device.
By fixing mobile responsiveness issues, you can improve the user experience on your website and ensure that it's optimized for all devices.
5. Security Issues
If your website has security issues, it can harm your users and business. Security issues include malware, phishing scams, and insecure login pages. Security breaches can lead to the loss or theft of sensitive information, such as personal data, financial details, and login credentials.
This can result in severe consequences for both your users and your business, including identity theft, financial loss, and damage to your reputation. In addition, if your website is hacked, it may compromise other websites and servers connected to it, causing even greater harm.
How to fix security issues?
To fix security issues, you can start by using a website security scanner to identify any vulnerabilities on your website. You can also try using secure hosting, prioritizing features like those found in ecommerce hosting providers, such as robust firewalls, intrusion detection, and regular backups, implementing HTTPS encryption, and using strong passwords for any login pages.
Additionally, it's a good idea to ensure that your website's users are educated on staying safe online. This can include providing information on identifying phishing scams, using two-factor authentication, and regularly updating passwords.
6. Cross-Browser Compatibility Issues

Cross-browser compatibility issues arise when a website is designed to work optimally on one browser but not on others. Since different browsers have varying levels of support for web technologies and standards, what may work on one browser may not work on another. For example, the latest version of Chrome may be able to handle certain website features, but the same features may not work on an older version of Internet Explorer.
How to fix cross-browser compatibility issues?
To fix cross-browser compatibility issues, you can start by testing your website on different browsers and devices. You can also use a tool like BrowserStack to test your website simultaneously on multiple devices and browsers. Additionally, using web standards and avoiding browser-specific code is a good idea to ensure your website is as compatible as possible.
7. Accessibility Issues
Accessibility is an essential aspect of web design that ensures all users, including those with disabilities, can access and use your website. Here are some common accessibility issues and how to fix them:
Poor color contrast: Users with visual impairments or color blindness may have difficulty reading text if the color contrast is poor. To fix this, you should ensure that the text and background colors have a high enough contrast ratio. You can use online tools such as the WebAIM Contrast Checker to test the color contrast of your website.
Lack of alt tags on images: Alt tags provide a text alternative for images, which is important for users who are visually impaired and rely on screen readers. To fix this issue, you should add descriptive alt tags to all images on your website.
Poor keyboard navigation: Some users may be unable to use a mouse and rely on keyboard navigation to access your website. To ensure your website is keyboard-friendly, you should ensure all interactive elements, such as buttons and links, are easily accessible via the keyboard. You can use the Tab key to navigate through your website and ensure all elements are highlighted logically.
Inaccessible multimedia content: Users with hearing impairments may have difficulty accessing multimedia content, such as videos or audio clips if they are not properly captioned or transcribed. To make your multimedia content accessible, you should provide captions or transcripts for all audio and video content.
8. SSL Certificate Error
An SSL certificate error occurs when there is an issue with the SSL certificate installed on a website. SSL certificates encrypt the communication between a user's browser and the website, ensuring secure data transmission. There are several types of SSL certificate errors that users may encounter:
Invalid SSL Certificate: This error indicates that the SSL certificate is not valid or has expired.
Certificate Name Mismatch: This error occurs when the domain name on the SSL certificate does not match the website's domain.
Untrusted SSL Certificate: This error appears when the SSL certificate is not issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) or is self-signed.
How to fix SSL certificate errors?
1. Check certificate validity: Ensure that the SSL certificate is still valid and has not expired. Most certificate authorities provide tools to check the validity of certificates.
2. Install a trusted SSL certificate: Obtain an SSL certificate from a reputable certificate authority and ensure it is properly installed on your web server. Follow the instructions provided by the certificate authority for installation.
3. Correct certificate name mismatch: If you receive a certificate name mismatch error, ensure the certificate's domain matches the website's domain. Obtain a new certificate with the correct domain name if necessary.
4. Update intermediate certificates: Intermediate certificates establish the trust chain between the SSL and root certificates. Make sure all necessary intermediate certificates are properly installed on the server.
5. Renew or update the SSL certificate: If the SSL certificate has expired or is no longer considered secure, renew it with the certificate authority or obtain a new certificate.
6. Force HTTPS: Configure your web server to redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS to enforce secure connections.
9. DNS Resolution Errors

DNS (Domain Name System) resolution errors occur when a domain name cannot be translated into its corresponding IP address. This can prevent users from accessing a website because their devices cannot locate the hosting server.
1. NS Server Unreachable: This error indicates that the DNS server responsible for resolving the domain name is not responding.
Solution: Check your network connection and ensure you can reach other websites. If the problem persists, try using a different DNS server, such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1). You can change your DNS server settings on your device or router.
2. DNS Server Misconfiguration: In this case, the DNS server is reachable but is misconfigured, leading to incorrect or incomplete DNS resolution.
Solution: If you manage the DNS server, review the configuration settings, including the DNS zone records, and ensure they are accurate. Verify that the DNS server software is up to date. Contact their support for assistance if you use a third-party DNS service.
3. Incorrect DNS Settings on Client Devices: The DNS settings on the user's device may be misconfigured, preventing proper DNS resolution.
Solution: Verify the DNS settings on the device. Ensure the device is configured to obtain DNS server addresses automatically (usually done through DHCP) or manually enter the correct DNS server addresses provided by your ISP or network administrator.
4. DNS Cache Issues: DNS resolution errors can occur if the DNS cache on the user's device or the DNS resolver server contains outdated or incorrect information.
Solution: Clear the DNS cache on the user's device. You can do this by flushing the DNS cache through the command prompt or terminal. Additionally, if you manage the DNS server, you can clear the DNS cache.
5. DNS Propagation Delay: When making changes to DNS records, it may take some time for the changes to propagate across all DNS servers globally.
Solution: Be patient and wait for DNS propagation to complete. This process typically takes a few hours, but it can sometimes take up to 48 hours. You can check the DNS propagation status using online tools specific to DNS propagation checking.
6. Domain Name Misspelling: Users may encounter DNS resolution errors if they input the domain name incorrectly.
Solution: Double-check the domain name spelling and ensure it is entered correctly in the browser's address bar.
Conclusion
Addressing these common website errors can improve your website's functionality and overall user experience. Whether it's broken links, poor navigation, or slow loading speeds, fixing these issues can help improve your website's performance and ultimately lead to more conversions and business success.
Remember, your website is often the first impression users have of your business. With a little effort and attention, you can create an error-free website that provides a positive user experience that will keep your users coming back for more.


 Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.