
No matter what industry you work in, your customers need to trust you. And, with 70% of internet users now taking various steps to protect their digital footprint online, your website must be secure.
As online shoppers become more security-savvy and demand more from online services, an SSL certificate error has the power to lose valuable website visitors and ultimately reduce sales. Adopting SSL certificates is fast becoming the best practice for websites worldwide. Here's why.
What is an SSL Certificate?
Short for Secure Sockets Layer, SSL certificates are digital files that provide websites with an encrypted HTTPS connection between a web browser and a server. In the simplest terms, a lock on the browser bar shows that a website has an SSL certificate to indicate its trustworthiness.
But how exactly does it do this? Acting as a security barrier, an SSL certificate sits between the browser and server and helps them to 'talk' to one another to keep users completely secure at all times. This helps protect user data, verify the website's identity, and positively impact user trust and brand perception.

How it works:
- Visitor enters an HTTPS address into the browser.
- Server shares an SSL certificate and a public key.
- Browser verifies the SSL certificate.
- Browser sends encrypted data and a secret key to the server.
- Server decrypts the data and receives the secret key.
- Web browsers and servers share encrypted data using a shared secret key through an end-to-end encrypted connection.
Also known as Transport Layer Security (TLS), SSL certificates contain a country code to prove the identity of the organization that owns the certificate, which can also be used to ensure the certificate is used in the correct location. But whether you're using Chinese or Canadian domains, the process is the same.
What is an SSL Certificate Error, and What Causes It?
SSL certificate errors happen when a browser can't confirm an SSL certificate is set up on a website. When users run into SSL certificate errors, browsers like Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox mark them as insecure and issue warnings to users.
Many things cause SSL certificate errors, the most common being that the SSL certificate is invalid. This can be for several reasons: typically, the certificate has expired, it has been revoked due to a security issue, or it's not trusted because it wasn't uploaded to the server properly. Quick fixes here include renewing, replacing, or reinstalling the SSL certificate.
Pro tip: Constantly monitoring your SSL certificate for any problems helps you fix them quickly so your website visitors don't encounter issues.
7 Common SSL Certificate Errors and How to Fix Them
Other common SSL certificate errors to watch out for include:
1. Domain Name Mismatch
A name mismatch error happens when the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) of the SSL certificate doesn't match the domain or the browser address bar. Companies with a presence in the UK might buy .co.uk domain names rather than sticking with their existing .com addresses. But if they forget to register all possible address variations - for instance, registering for domain.co.uk but not https://domain.co.uk/ - an SSL certificate error will appear.
To fix domain name mismatch SSL errors, ensure all subdomains and IP addresses are included on the certificate. You can also update the SSL certificate to secure multiple hostnames or domains under one certificate. It may also be worth setting up a redirect to direct users to the correct URL.
2. Untrusted Certificate Authority (CA)
Browsers have lists of built-in trusted certificate providers. So, if the SSL certificate is approved by an authority that isn't on the list, the browser deems it untrustworthy and triggers this common SSL error. Self-signed certificates (signed by the server itself) and expired SSL certificates can also cause SSL certificate authority errors.
If the certificate has expired, the answer may be as simple as updating or renewing it. Ensure the server displays the entire certificate chain and always uses SSL certificates issued by recognized and trusted Certificate Authorities (CA). Google operates its own Certificate Authority called Google Trust Services, while Verisign, DigiCert, and Entrust are automatically trusted by most browsers.

3. Incomplete Certificate Chain
This SSL error occurs if the certificate is missing intermediate or root certificates. To fix it, identify the incomplete chain, contact the CA issuing your SSL certificate, and obtain the intermediate certificates. Once you have these, update the SSL configuration on your server, and you should be up and running again.
4. Mixed Content
Sometimes, online resources like images, scripts, or stylesheets loaded over an unsecured HTTP connection can get mixed up over a secure HTTPS connection. To fix mixed content errors, first, you must identify which files are causing the error. Most browsers have built-in developer tools which can be used to identify resources being loaded over HTTP quickly.
If you're accessing the website through a personal IP VPN, ensure the VPN configuration doesn't introduce mixed content issues.
Once you've identified the source(s), update all the HTTP URLs to HTTPS instead. If you use a content management system, links in databases, or content delivery networks, it's important to check that the base URL is configured with HTTPS.
5. Insecure Cipher Suites
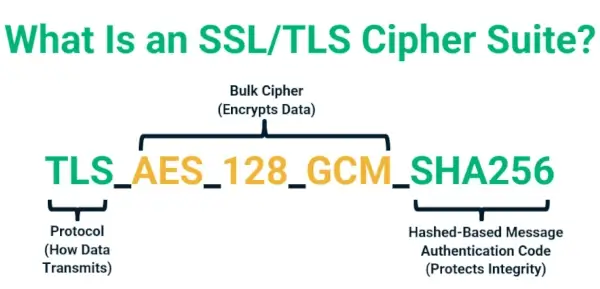
A cipher suite is a set of coded algorithms that essentially allow browsers and web servers to talk to each other securely. Incompatible or outdated cipher suites, misconfigurations, and network issues can all result in this common SSL error.
Put a stop to this error by updating your server configuration and turning off any obsolete cipher suites. Keep web server and client security software up to date and conduct regular security audits to proactively identify and address any vulnerabilities in the future.
6. HSTS Issues
Short for HTTP Strict Transport Security, HSTS is a widely supported web security standard that makes sure browsers always connect over a secure HTTPS connection. This is particularly important if you take online payments or data that needs to be kept safe.
Often caused by HSTS misconfigurations and expired HSTS policies, ways to fix common HSTS errors include checking HSTS Head configurations, renewing or updating SSL certificates, addressing clock discrepancies, and checking browser cache issues.
7. Outdated Browser

The "Outdated Browser SSL Certificate Error" is usually displayed when users attempt to access a website with an outdated or unsupported web browser that doesn't accept SSL certificates.
Web administrators should check browser compatibility with the SSL certificate, verify SSL settings on the server, update outdated root certificates, and implement fallback mechanisms to support older browsers. It's also worth adding clear messages to key areas of your website to encourage visitors to update their browsers for better levels of security.
Summary
|
Common SSL Error |
Likely Cause |
Solution |
|
Name Mismatch |
|
|
|
Untrusted Certificate Authority |
|
|
|
Invalid Certificate Chain |
|
|
|
Mixed Content |
|
|
|
Insecure Cipher |
|
|
|
HSTS |
|
|
|
Outdated Browser |
|
|
Final Thoughts
Today's consumers want a secure experience, and SSL certificates ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data transmitted between users and their favorite websites. This is especially important if you work in an area where security is vital. Going to your website and seeing a security issue is a surefire way to drive your potential customers to competitors.
As consumers become more security conscious, website owners must take the time to invest in addressing common SSL certificate errors such as these as part of their ongoing website security strategy to keep customers satisfied, happy, and loyal for the foreseeable future.


 Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.