Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are among some of the most exciting technological revolutions of our time. An increasingly ubiquitous aspect of our digital environment, AI is changing how we interact with our devices and surf the internet.
Most of us fall somewhere between the two poles of a utopian and a dystopian understanding of the new technology, seeing both its benefits for society and its inherent risks. Website security is one area where these two sides of the story intertwine, the benefits and the risks both creating and contradicting each other.
Before looking at how AI is fortifying website security, this article will cover some of the threats that make AI cybersecurity necessary.
The Rise of the AI Cyberattack
The history of cybersecurity is completely entwined with the history of cybercrime. Cybercriminals and malicious hackers have often been among the first to start using new digital technology. They are in a constant cat-and-mouse game with the security professionals whose job is to prevent them from causing damage.
It should come as no surprise that such professionals have been quick on the uptake of AI as a tool for their crimes. Consider denial of service attacks as an example. These have evolved from the simple shell scripts of the early 2000s to today's AI-powered-DDoS attacks coordinated across a distributed network of hundreds or even thousands of compromised computers.
A DDoS attack works by flooding a web application with requests, thus causing it to fail. Whereas attacks on websites that use techniques like SQL injection or DNS hijacking tend to be oriented towards website defacement, DDoS attacks are typically intended to cause significant downtime.
An appropriate analogy from the call-center business would be if we imagined a call park intentionally filled up with fake incoming calls, meaning that anyone who was actually trying to call the given number would not be able to get through.
In a classical DDoS attack, the compromised network known as a bot is directed by a human working the command and control server to orchestrate the attack. What part of the application stack is being flooded can then be adjusted to respond to the target application's security procedures.
Recent DDoS attacks have responded to advances in website security by employing machine learning AI models called artificial neural networks. These attacks are fully automated, changing vulnerability types and attacking vectors based on the response from the defense side without human intervention.
Automated Vulnerability Testing
Since its inception, the discipline of cybersecurity has been in a constant game of hide-and-seek with malicious hackers. Web vulnerability testing tries to anticipate cyber-attacks by searching out a web service's vulnerabilities in the hopes of rectifying them before they are discovered and exploited by the wrong people.
Vulnerability testing should mirror the latest developments in malicious hacking if it is to have any hope of preventing attacks. These days that means appreciating AI and machine learning as both a threat-side risk and a defense-side resource for cybersecurity.
It can sometimes feel like an impossible task to keep up with the pace of digital technologies. From websites to your business phone line app, Internet-based services are constantly adding new features and plug-ins that can change the internal architecture of applications, causing new vulnerabilities to arise.
AI can help find bugs and alert you to potential security weak points before they endanger the larger systems, often more efficiently than human developers.
On the one hand, we can use AI to update security databases automatically. Analyzing different logs and records can identify new malware threats from volumes of data a human could never hope to sift through. On the other, it can scan your system for unusual activity which might highlight an attempted attack.

AI Security Solutions
As well as helping to identify threats, AI can actually automate the bug-fixing and security-patching process. AI is now incorporated into many antivirus software solutions, helping to streamline damage control by automating the removal of viruses and patching security flaws.
Returning to the contact center analogy, imagine that instead of allowing a parking system to be overwhelmed by incoming calls, call center quality was maintained by automatically rejecting, diverting, or quarantining ingenuine calls.
This is increasingly the scenario when it comes to the automatic detection of anomalous behavior. For example, banks and credit card companies will often automatically block transactions flagged as suspicious by AI.
For website security, the same type of procedures can block log-in attempts from unfamiliar browsers and automate identity verification. AI has also been applied to the task of password generation and detecting if passwords have been compromised. These types of applications of AI are geared not towards the integrity of the system as a whole but individual web user's safety.
Today's biggest content management systems (CMS) are designed to be fully customizable with many AI functions built-in to make web design easier.
From a security perspective, AI is helping to keep the CMS ecosystem safe by ensuring the latest security protocols are implemented across the board. These days, responsibility for updates lies less with individual developers but is instead delegated to automated whole-system upgrades.
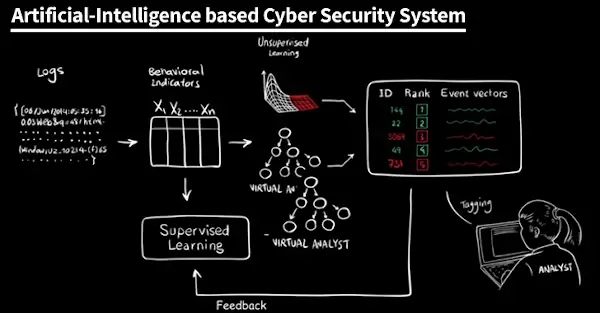
Ultimately, like intelligence itself, AI is nebulous and a hard to pin down concept. For website security, it is worth remembering that rather than defining a single coherent technology like the artificial neural network, AI refers to a whole host of different innovations and their applications.
Practitioners of website security would do well to distinguish between three different types of machine intelligence if they want to make the most of advances in AI.
- Assisted intelligence is designed to provide the best information for human decision-makers.
- Augmented intelligence is more of a tool for responding to challenges that allow people to do things they couldn't do otherwise.
- Autonomous intelligence describes models that can act on their own, making decisions without any human intervention.
The most effective cybersecurity posture uses all three levels of AI to maximize its usefulness for protecting web applications and preventing attacks. The best approach will depend on your specific priorities.
If you are working in e-commerce security, then preventing financial fraud might be your biggest challenge. But if your website is more content-oriented, then maintaining uptime is likely to be your main goal.
Knowing what technology to use and in which instance is the key to a good website security strategy. In this respect, AI is no different from other tools for digital security.


 Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2000-2025, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.